Hydrogen is green and is an ideal zero-carbon energy source.
However, hydrogen is currently produced mainly from petroleum, and the cost is very high. Scientists have been exploring whether they can use the ready-made “equipment†in nature to make hydrogen.
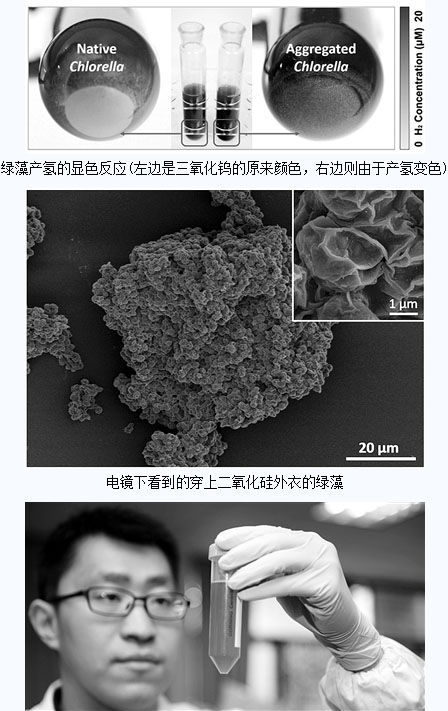
Researchers from Zhejiang University have put a layer of silica “cloth coat†on the green algae cells through interdisciplinary cooperation, enabling them to continuously use photosynthesis under natural conditions to efficiently produce hydrogen, producing 17 ml per liter of green algae. hydrogen. This is an important breakthrough made in the field of bio-photosynthetic hydrogen production. It provides a brand-new idea for the transformation of photosynthetic organisms by chemical means and the realization of hydrogen production by photobiology.
Related papers were published in the recently published German "Applied Chemistry".
More than 30 years ago, scientists discovered that there was a hydrogenase in Chlorella cells. When it is activated, green algae can produce hydrogen when photosynthesis occurs.
"However, hydrogenase is very sensitive to oxygen. Under normal lighting conditions, hydrogenase will rapidly lose its activity. Green algae produces only oxygen." On November 9th, Associate Professor Xu Xurong, the head of the research group, said in an interview with a reporter from Science and Technology Daily. Hydrogenase is activated to produce hydrogen, which is a stress response produced by green algae in response to hypoxia.
Is it possible to transform green algae, isolate oxygen and wake up hydrogenase?
One of Xu Xurong’s collaborators, Professor Tang Ruikang of Zhejiang University’s Department of Chemistry, has a unique ability to “coat†cells with bio-mineralization means to impart new properties to cells without altering their original properties.
If Chlorella is also “wrappedâ€, can it be artificially created in an oxygen-deficient environment?
The task force tried to use silica to remove green algae.
The experiment has found an interesting phenomenon: When the green algae “wearing†the silica coat gradually adhere together to form a green algal agglomerate, the scientists used the probe to detect the green algae above the test tube. Oxygen was detected and hydrogen was also detected.
Experiments have confirmed that green algae can continuously produce hydrogen under normal light conditions. The longest time is up to 72 hours.
“Under the electron microscope, we see a green algae complex about 100 microns in diameter containing about 5,000 or so green algae,†explained Xiong Wei, a doctoral student in the research group.
At present, the research team is trying to solve the problem of uncontrolled growth of green algae. "After 72 hours, if there are more and more green algae in the group, the green algae will be dissolved and the hydrogen production process will stop." Xiong Wei said that they are looking for new ways to control the propagation of green algae. It is one step closer to industrial application. (Correspondent Zhou Wei reporter Lin Lijun)
Lifting Point,Lifting D Rings,Hoist Ring,Swivel Hoist Ring
Shandong Shenli Rigging Co.,LTD. , https://www.shenliriggingcn.com