Naipu ISW end suction pumps designed in accordance with ISO2858 standard,are single-stage single-suction horizontal centrifugal pumps featured by integrated simple construction for less space, easy installation, smooth operation with less noise and free of daily maintenance due to the introduction of high quality mechanical seals and closed coupling.
Typical Applications---
Water supply system
Lowering underground water level
Boosting
Gardening and aricultural irrigation
Various kinds of industrial application
ISW End Suction Pump Configuration Drawing
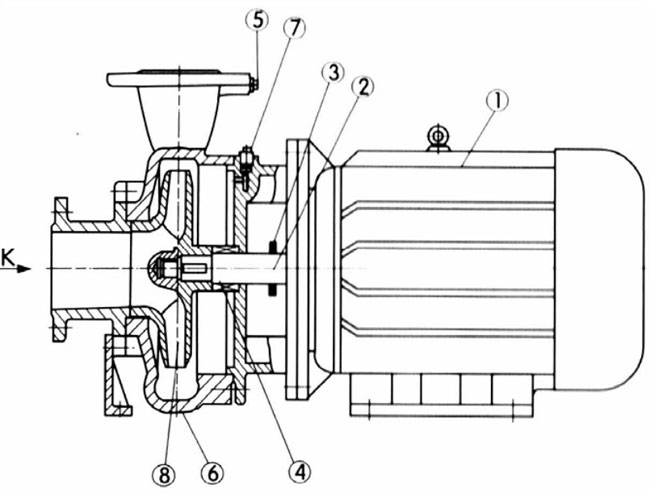
Main Part Number At The Drawing
|
1 Motor
2 Shaft 3 Deflector 4 Mechanical Sea |
5 Pressure Monitoring Hole
6 Pump Casing 7 Pressure Release Plug 8 Impeller |
ISW END SUCTION PUMP SELECTION CHART
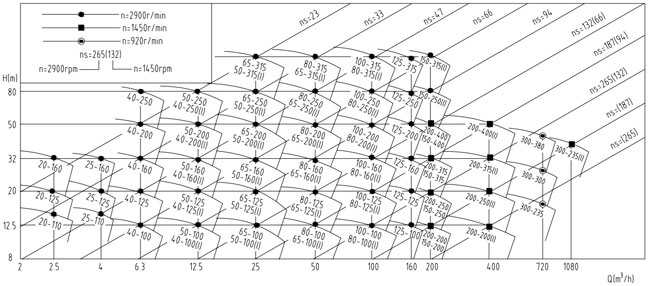
NP- ISW END SUCTION PUMP PERFORMANCE PARAMETERS
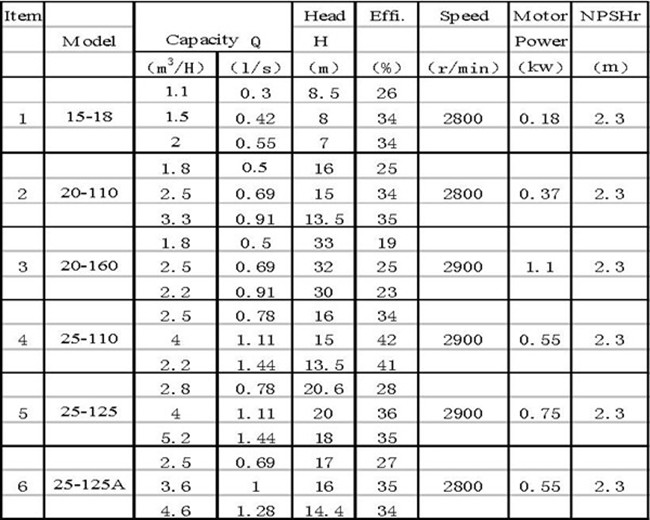
ISW End Suction Pump,End Suction Pump,Clear Water Pump,End Suction Water Pump
Shijiazhuang Naipu Pump Co., Ltd. , https://www.naipu-pump.com